Germany is reportedly working on reducing the nation’s economic dependency on Communist China due to concerns about “human rights abuses and the risks of being beholden to an increasingly assertive authoritarian state,” Reuters reports. Berlin finally learned one lesson from Russia’s invasion of Ukraine: it’s dangerous to economically rely on authoritarian regimes.
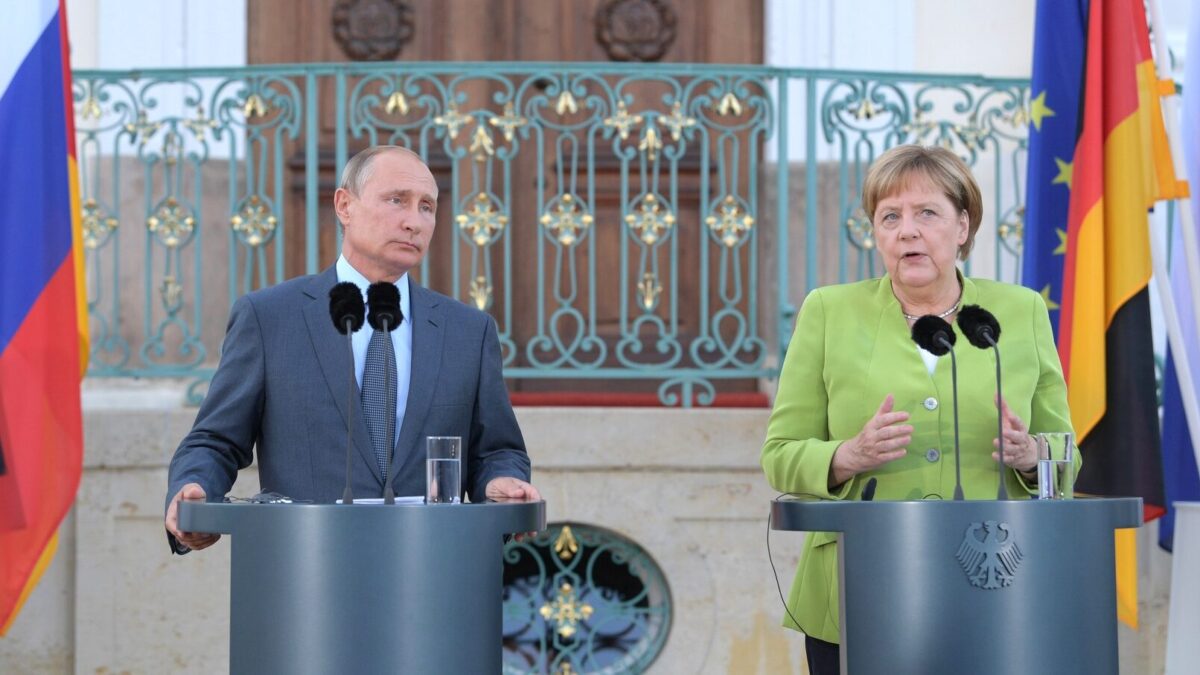
Former German Chancellor Angela Merkel’s policies — building an economy based on Russia’s energy supply and China’s market demand — were primarily responsible for German’s economic predicament today. Zealous in fighting climate change, Merkel shut down coal mines and retired the majority of nuclear power plants in Germany while relying on Russia for energy and raw materials, despite repeated warnings from the Trump administration. By 2020, Russia supplied more than half of Germany’s natural gas and about a third of all the oil that Germans burned to heat homes, power factories, and fuel vehicles.
While paying Russia billions of euros for energy supply (the money no doubt helped finance Putin’s war chest), Merkel neglected to invest in German’s armed forces, even after Putin annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. She outsourced Germans’ and, to a larger extent, Europe’s security to the United States and simply hoped for the best. When Merkel retired in 2021, after being in office for 16 years, German’s military was left “in a weak position and require years of renewal to become a credible deterrent to Russian aggression,” according to The American Institute for Contemporary German Studies.
Strengthened China Ties
Besides empowering and enriching Russia, Merkel was keen on strengthening Germany’s economic ties with China while in office. No other leaders from Western democracies had visited China more often than Merkel (she had 11 state visits to China).
To promote Germany’s export-oriented economy, Merkel was indifferent to China’s aggression in the South China Sea, its geopolitical expansion through the “Belt and Road” infrastructure project, and its increasingly assertive foreign policies. In addition, she avoided criticizing China’s mishandling of Covid-19 in the early days of 2020 and turned a blind eye to many human rights abuses in China, especially the genocide of Uyghur Muslims and suppression of the pro-democracy movement in Hong Kong.
Under Merkel, China became Germany’s largest trading partner in 2016. German’s auto industry especially relies on China — about 50 percent of German car maker Volkswagen’s profit comes from China. Merkel’s China policy has made Germany’s economy vulnerable and helped speed up the Chinese military’s modernization.
Beijing reportedly focused on investments in Germany to obtain critical technologies, especially those with dual-use, meaning both civilian and military applications. For example, engines made by German companies have powered several types of Chinese navy warships, Deutsche Welle found.
Although Merkel retired in 2021, the effects of her economic policies continued. According to a German Economic Institute (IW) study, Germany’s economic dependency on China has continued to grow in 2022. “China’s share of German imports rose to 12.4 percent in the first half of 2022, compared with only 3.4 percent in 2000. German imports of Chinese goods… have surged by 45.7 percent year-on-year in the comparable period of the first six months. Germany’s trade deficit with the country had leapt to almost EUR 41 bn by mid-2022.”
A Wake-Up Call
After Russia invaded Ukraine, Germany joined other EU nations in imposing punitive economic sanctions on Russia. Putin retaliated by weaponizing his energy supply to Europe, sending energy prices soaring and dealing a blow to the German economy.
Inflation in Germany has reached a 40-year high. Suppose Putin shut off the natural gas supply to Europe, as he threatened. In that case, many predict an energy-induced recession in Europe is inevitable, and Germany could lose close to $240 billion in economic output over the next two years.
The grim economic outlook, and the fact that Beijing refused to condemn Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and helped Russia evade the West’s economic sanctions by purchasing Russian energy and agriculture products, have become a wake-up call for Germany. Additionally, Beijing’s “zero-Covid” policy that has kept dozens of cities and millions of Chinese people in lockdown means German businesses have had limited access to the Chinese market, and the trend will continue in the foreseeable future.
The German Economic Institute called for the government to change its economic policy, “specifically a reduction in incentives for doing business with China and a shift towards more trade with other emerging markets.” It also warned German businesses to “curb their dependency on China.” Otherwise, companies may expose themselves to bankruptcy due to Western sanctions imposed on China in the event of the People’s Liberation Army’s invading Taiwan.
Deutsche Bank CEO Christian Sewing also warned, “When it comes to dependencies, we also have to face the awkward question of how to deal with China.” He appealed to the German government to decouple economically from China and acknowledged such a move would “require a change no less fundamental than decoupling from Russian energy.”
Germany Stepping Back
These calls for action have reached their desired audience. Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock acknowledged Germany couldn’t afford to “just behave following the motto ‘business first,’ without taking into account the long-term risks and dependencies.”
Reuters reports that Germany’s economic ministry is considering several actions to cut Germany’s reliance on China, including reducing or scrapping investment and export guarantees for China and no longer promoting trade fairs and manager training there. It is also contemplating screening not just Chinese investments in Germany but also German investments in China. It also might submit a complaint to the World Trade Organization about unfair Chinese trade practices, together with the Group of Seven, an intergovernmental political forum consisting of Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
While Germany is waking up to the risks of economic dependency on authoritarian regimes, the Biden administration has deepened our nation’s economic reliance on China with a green revolution that centers around replacing fossil fuels with solar and wind, and gas-powered cars with electric vehicles (EVs). China dominates the global supply chain of raw materials and parts for EV batteries, solar panels, and wind turbines. The nation has been able to keep the manufacturing cost low by burning coal and employing forced labor from Uyghur and other ethnic minorities.
Even Politico has had to admit the dirty truth: “The U.S path to clean energy goes straight through China.” Germany’s economic woes should serve as a timely warning to the Biden administration that relying on an authoritarian regime is both dangerous and foolish.